What do you have to know about herpes
The spread of herpes infection is due to the high resistance of the herpes virus to various environmental factors, long-term viral carriage and the diversity of routes of transmission. 95% of the world’s inhabitants are carriers of different types of herpes virus. Herpes infection is referred to as an opportunistic infection, because it is clinically manifested only when exposed to certain adverse factors. Once activated, herpes infection can be latent or in acute and/or chronic form. Immunodeficiency states may lead to generalized infection. According to German researchers, the incidence of labial herpes in persons over 35 years of age was 20-30%.
If you want to buy herpes medications, hair loss drug or other medications, you can buy everything you need online.
Types of herpes
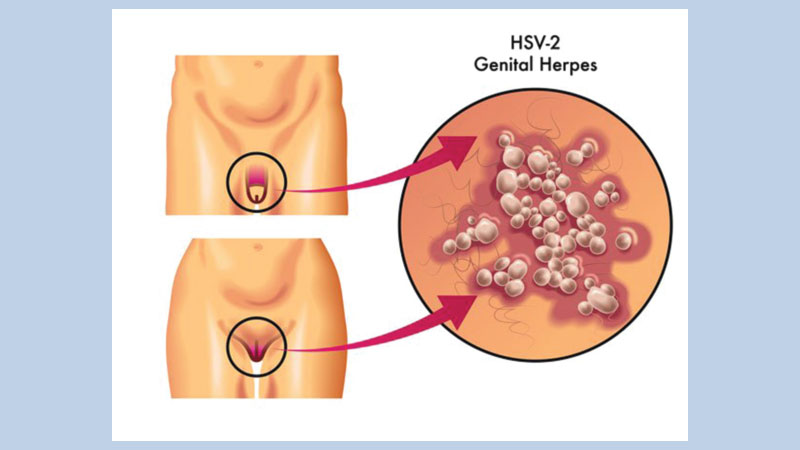
To date, eight types of herpes virus are known. The most common are herpes simplex virus type 1 (HPV-1) and herpes simplex virus type 2 (HPV-2). HPV-1 is associated with labial herpes, herpes of the mucous membranes and skin; with HPV-2 – genital and neonatal herpes.
During primary infection, HPV-1 enters the mucous membranes of the lips or oral cavity and multiplies at the site of infiltration, resulting in vesicular rashes. The virus then spreads – it penetrates the nerve endings, migrates within the nerve fibers, becomes latent, and persists in the body.
Herpes infection throughout a person’s life can manifest itself only once. But in some people, the disease becomes recurrent and sometimes chronic.
Activation of the virus persisting in the body leads to a recurrence of herpes infection and is caused by a number of factors: stress, ultraviolet radiation, cyclic changes in hormonal status (menstruation), pregnancy, infectious diseases accompanied by fever, therapy with immunosuppressive drugs, etc.
Under such conditions, the development of herpes infection does not depend on the state of the immune system, as the herpes virus spreads inside nerve cells and does not come into direct contact with specific antibodies of blood plasma, serous and tissue fluid. Clinically, herpes infection is manifested by the development of edema and erythema of varying severity on the skin and mucous membranes. It should be noted that carriers of the virus (who have no symptoms of the disease) are often carriers of the infection. In adults, primary infection is often manifested by labial herpes and acute pharyngitis. The most serious complication in children and adults is encephalitis, which can be fatal if not treated in time.
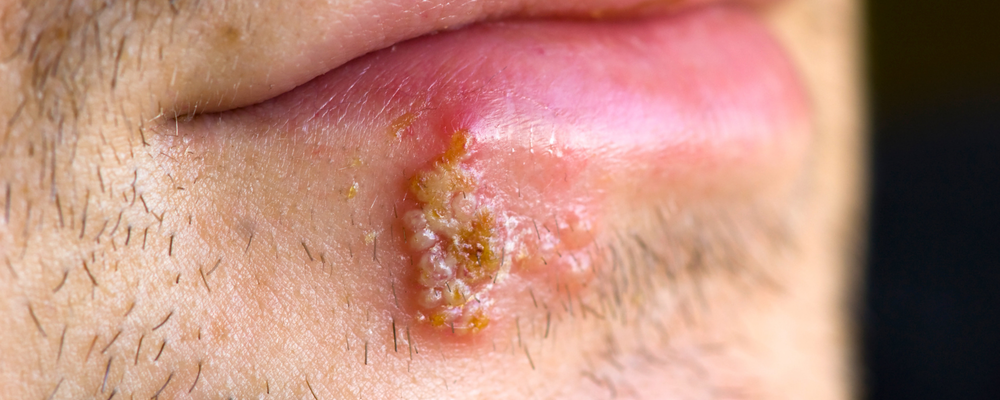
Herpes infection is characterized by four stages of clinical manifestations: onset of relapse, inflammation, ulceration, and crusting.
- The first stage (onset of relapse) is itching of the mucous membranes of the lips, tongue, and facial skin. The development of the disease can be prevented if antiviral medications are used at this stage.
- Stage 2 (inflammation) is the appearance of erythematous rashes, which are subsequently replaced by clustered blisters with clear serous contents.
- The third stage (ulceration) – blisters open with the formation of erosions. At this time, the patient is very infectious.
- Stage four (crusting) – loose crusts form over the erosions. If the rules of personal hygiene are not followed, the virus can affect the eyes, skin of the fingers and hands (herpetic eczema), genitals, etc.
HPV adversely affects pregnancy and childbirth, sometimes causing fetal abnormalities, miscarriages, generalized herpes infection in newborns, etc. Herpes infection can activate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and lead to the progression of AIDS. If you start using the best herpes medication in time, you will be able to get rid of its symptoms quickly.
